User Guide¶
Accessing the Jetson console¶
Warning
Do not run the Jetson SOM without a heat sink. The lid of the Donington system is the primary heat sink, and running the Jetson with the lid off may result in shut down or throttling. If you need to run the system for a continued period of time with the lid removed, position a fan to move air over the heat spreader installed on the Jetson module.
Open the lid of the Donington system, to expose the inner electronics.
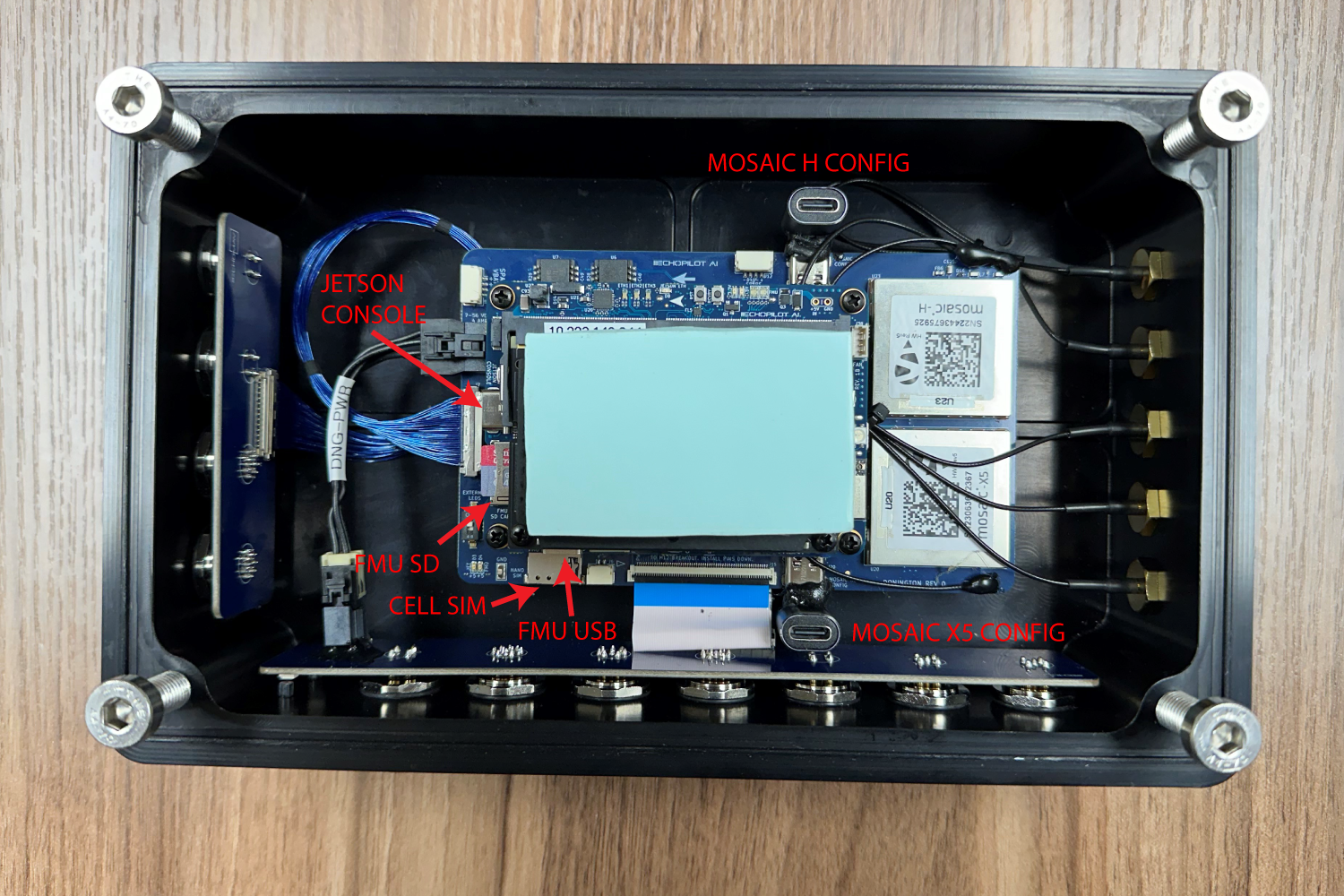
Note
A thermal pad is positioned between a heat spreader on the Jetson and the Donington system lid. Please ensure this is in position and undamaged after removing and replacing the lid.
Attach a USB cable between your host computer and J15 (Console) on the EchoPilot AI Board. A USB-C right angle adapter may be useful. Such adapters are included with the hardware or can be obtained elsewhere.

In step 2, your host computer should have enumerated a virtual comm port. You will now need to find the name of the port.
Info
On Windows: Open Device Manager (Start → Control Panel → Hardware and Sound → Device Manager) Look in the Device Manager list, open the category "Ports", and note the COM port added USB Serial Port (COM?) (e.g., COM10).
On Linux: Run dmesg -w and then plug in unplug and replug in the USB cable. You should see the name of the device added, typically FTDI USB Serial device converter now attached to ttyUSB? (e.g., ttyUSB0).
Use a terminal program to connect to the Jetson's console at 115200 baud, 8N1.
Info
On Windows: We recommend Putty or TeraTerm.
On Linux: We recommend Picocom. Install with sudo apt-get install picocom. Use with picocom /dev/ttyUSB? -b 115200. To exit picocom, use Ctrl-a Ctrl-x.
Power the Donington System 13-36VDC source capable of supplying up to 4A.
Warning
If using a bench supply with over-current protection, we recommend turning it OFF. The boot process requires short bursts of high current and over-current protection on some supplies will result in a failed boot. In most cases, if the Jetson fails to boot it is due to a poor power supply.
You should now see the boot messages in your console, and once boot is complete, you will see a login prompt.
Note
The default username is echopilot and the default password is echopilot
Success
At this point you are logged into the Jetson.
Accessing the Jetson via network¶
The Donington system has two 100Mbps Ethernet ports (ETH1 and ETH2). Upstream, these go to a network switch, so either one can be used to access the Jetson SOM. An M12 to RJ45 cable is required (e.g. ASI-M12-RJ45-11101)
EchoMAV's standard provisioning sets the Jetson module to a static IP address provided on the label with the device. There is also an alias ip of 192.168.253.0 which can be used if you do not know the static IP.
To gain console access to the Jetson over the network, use ssh from a terminal session on the host computer:
Note
The default password is echopilot
Note
If the label is damaged, or the static IP has been inadvertently changes, you can use the configuration IP "backdoor" alias of 192.168.154.0/24 to access the system. Ensure your host system is in the 192.168.0.0/24 subnet (any valid IP address not equal to 192.168.154.0 will work). Please refer to the instructions above for how to change your host IP address.
IP Configuration¶
The EchoPilot AI will be labeled from the factory with a static IP address in the 10.223.0.0/16 subnet such as 10.223.134.126 (for example only). If you do not know the IP address, you may be able to access the system using the backdoor/alias IP of 192.168.154.0/24.
During provisioning, the system's static IP address is calculated using the last two octets of the Jetson's eth0 interface MAC address with a netmask of 255.255.0.0 (/16). For example, given the MAC address of 00:30:1A:4E:A4:3E, the last two octets 0xA4 and 0x3E are converted from hex to decimal and then assigned as the last two octets of the IP address. In this example, this MAC address would correspond to 10.223.164.62/16 because 0xA4 = 164 and 0x3E = 62. This IP address is printed on the label from the factory.
Changing the IP Address¶
To change the Jetson's IP address, first gain console access via USB (internally in the box), then follow the steps below to change the configuration to either DHCP or a different static IP address. Making these changes when connected to the Jetson over the network will likely result in you losing your connection as the Ethernet interface goes up/down.
Configuring for DHCP¶
If you wish to use DHCP, follow the instructions below:
Once logged in via the console, modify the existing static connection (e.g. "static-eth0") to be DHCP:
sudo nmcli con mod static-eth0 ipv4.method auto
sudo nmcli con mod static-eth0 ipv4.gateway ""
sudo nmcli con mod static-eth0 ipv4.address ""
sudo nmcli con down static-eth0
sudo nmcli con up static-eth0
Configuring or Changing the Static IP Address¶
If you do not have a DHCP server, or you wish to assign a static IP address to the Jetson, follow the instructions below.
First gain console access via the USB connector. Once logged in via the console, delete the default connection, for example "Wired connection 1":
Set up a static connection calledstatic-eth0 with an IP of 10.223.1.10, a netmask of 255.255.0.0 and a gateway of 10.223.1.1. The values are just examples, please adjust to the desired settings for your network.
Bring up the new interface
To verify network connectivity, ping another device on the network, or to verify internet connectivity, ping a Google DNS server:
Other NetworkManager tips and tricks¶
Linux for Tegra uses networkmanager (nmcli) for its network interfaces. Below you will find a few commands for common network tasks. These examples are not intended for you to follow sequentially, these are common examples which will demonstrate most network configuration needs.
Show connections:
nmcli con show
Example: Delete the default connection ("Wired connection 1") and set up a static connection called static-eth0 with an IP of 172.20.1.100, a netmask of 255.255.0.0 and a gateway of 172.20.2.100:
sudo nmcli c delete "Wired connection 1"
sudo nmcli c add con-name static-eth0 ifname eth0 type ethernet ip4 172.20.1.20/16 gw4 172.20.2.100
sudo nmcli c up static-eth0
Example: Change IP address of static-eth0 connection to 192.168.1.4 with a 255.255.0.0 (/16) netmask:
Example: Change the gateway of static-eth0 connection to 192.168.1.1:
Example: Change the DNS of static-eth0 connection to 8.8.8.8:
Example: Take down/up of static-eth0:
static-eth0 connection: Example: Add a new connection called static-eth0 with IP 172.20.2.22/16 and gateway 172.20.2.100 on interface eth0:
Example: Add a persistent route so that multicast traffic to 224.x.x.x goes to the static-eth0 connection:
Example: Change the static-eth0 connection to remove static IP and enable DHCP. In this case, it would be clearer to delete the connection since it is named static-eth0 and call it something else, but for edification:
sudo nmcli con mod static-eth0 ipv4.address ""
sudo nmcli con mod static-eth0 ipv4.gateway ""
sudo nmcli con mod static-eth0 ipv4.method auto
sudo nmcli con reload static-eth0
Connecting to the FMU via the USB connector¶
- Attach a USB cable between the host computer and the FMU USB connector (J7).
- Start a Ground Control application on the host computer such as QGroundControl or Mission Planner.
Info
QGroundControl: Will automatically connect.
Mission Planner: Select the appropriate COM port at the top right, 115200, then click CONNECT.
Cellular Modem Installation¶
The Donington system is compatible with Sierra Wireless M.2 3052 modems, such as the EM9191. Using other modems may not work without configuration changes due to the way other modems detect the presence of SIM cards and other critical functionality.
When installing a cellular modem, care must be provided to also install the heat sink kit. This kit works by placing a thermal bad under the modem, which couples heat to a copper pour on the Donington carrier board. On the top side of the Donington carrier board, a heat sink is placed using thermal conductive epoxy. Failure to properly heat sink the Cellular modem may result in throttling, especially during data uploads (such as video streaming).